Vitiligo: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment

Vitiligo is a chronic condition that causes the skin to lose color. The American Academy of Dermatology describes vitiligo as “more than a cosmetic problem” and one that requires medical attention. It can occur in all skin types and in people of all ethnicities, but it is very prominent in people with darker skin tones. Around 0.5% to 2% of the population is affected by vitiligo globally.
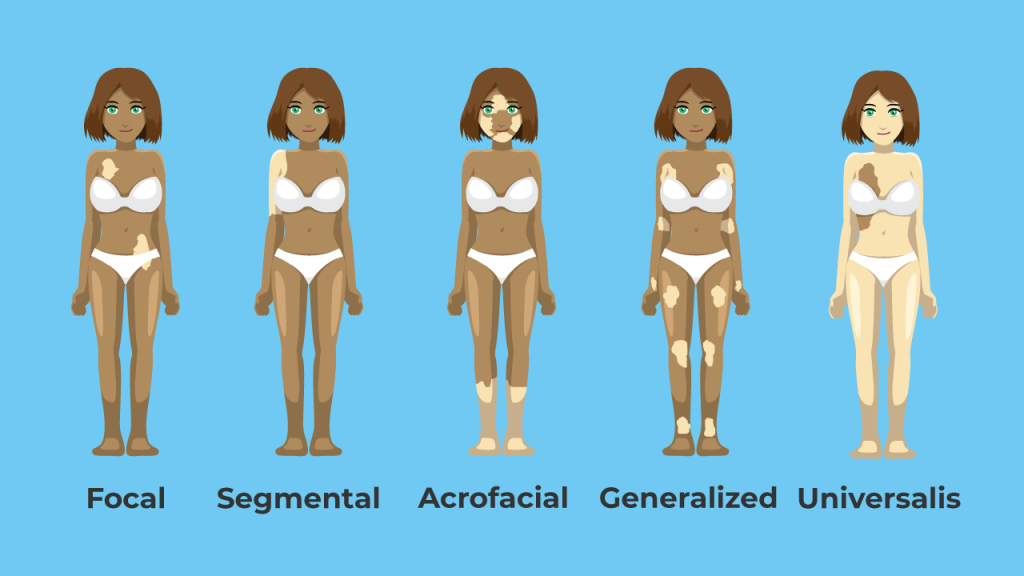
Types of vitiligo
There are five types of vitiligo
- Focal: Discoloration remains in one place and does not spread
- Segmental: Confined to a particular region of your body such as your face
- Acrofacial: Discoloration on the skin of the face, hands, and openings such as eyes, nose, and ears
- Generalized: Discolored patches show all over your body
- Universal: Eighty percent of the skin is discolored
Areas of body affected
Anyone can get vitiligo at any age. But it generally appears before the age of 20. The discoloration occurs in patches and may get bigger with time. It can cause premature greying of hair on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and beard area. It can cause discoloration inside the mouth and nose on the mucous membranes.
What causes vitiligo?
Melanocytes are cells in the skin which produce a pigment called melanin. This pigment is responsible for giving skin, eyes and hair its color. In vitiligo, the number of melanocytes reduces leading to low content of melanin, which leads to the development of white patches. The reason why the number of melanocytes reduces is not known, but the following have been implicated in the development of vitiligo:
1. Autoimmune conditions
Non-segmental vitiligo is considered to be an autoimmune condition. It is the most common type. Here the immune cells of the body attack melanocytes instead of attacking the foreign cells such as bacteria. You are at risk of developing non-segmental vitiligo if you have the following conditions:
- Family history of vitiligo
- Family history of autoimmune diseases
- Medical history of autoimmune disease
- Melanoma (skin cancer)
2. Neurochemicals
Neurons release certain chemicals at the nerve endings, which may be detrimental to the melanocytes. Segmental vitiligo is considered to be caused by these neurochemicals. It is not a very common type. The risk of developing segmental vitiligo is higher if you have the following conditions:
- Stressful events
- Skin damage due to severe sunburn
- Exposure to certain chemicals
3. Heredity
Vitiligo runs in a few families and a genetic connection has also been implicated.
Symptoms of vitiligo
- In most cases, patches of discoloration usually start first on hands, forearms, feet and face. But it may also start at other places in a few patients; premature greying or whitening of hair, eyebrows and beard
- Loss in the color of mucus membranes (tissues that line the oral cavity) inside the mouth and nose.
Diagnosis of vitiligo
The doctor observes the skin during a physical examination and may ask you to take the following tests:
- Skin biopsy: Small sample of your skin is sent to a laboratory for examination
- Wood’s lamp test: The doctor observes the patches of vitiligo under a UV lamp in a dark room. This enables the doctor to differentiate vitiligo from other skin conditions
- Blood test: Autoimmune conditions can trigger vitiligo. The doctor conducts blood tests to acquire more information on autoimmune conditions in the body.
Treatment of vitiligo
There is no cure for vitiligo. However, the progression can be slowed down by opting for treatments based on your age, type of vitiligo, and your needs. The following treatments have been tried with varying results:
Corticosteroids: Topical application of corticosteroids in the form of creams or gels may bring back the color. But it takes several months to see the results. It may also cause streaks and thinning of the skin. If the progression of vitiligo is fast, the doctors may prescribe oral medications or injections.
Phototherapy: Using ultraviolet A & B light can slow or stop the progression of vitiligo. This is generally used in combination with medicines such as Psoralen.
Depigmentation: This treatment includes depigmenting the skin regions that are not affected. This is done to mainly give a uniform cosmetic appearance. This is a permanent treatment but has side effects such as swelling, redness, itching, and dry skin.
Skin camouflage: Patients can camouflage the white patches with cosmetic creams or patches, which match their skin tone the best.
Immunosuppressant: Drugs known as calcineurin inhibitors help in suppressing the immune system, which is responsible for destroying the melanocytes. But results are not very consistent with these drugs.
Surgery: Skin grafting is done when none of the other procedures work. Here the surgeon transfers healthy portions of skin to discolored areas.
Doctors also recommend practicing the following to slow the progression of disease:
- Use sunscreen with at least SPF 30 and reapply it every two hours
- Stay away from tanning beds
- Do not get tattoos
Complications of vitiligo
Sunburn: Sunburn is red, hot and sore skin caused by overexposure to the sun. Normally the melanin in the skin absorbs the harsh sun rays protecting the skin. But in vitiligo, since the pigment is absent, the skin is unprotected by the effects of the sun.
Eye issues: Eye issues such as iritis (inflammation of the iris) and uveitis (inflammation of the middle layer of the eye) as the melanocytes in the eyes are destroyed.
Also read: Eye Health: Tips for Maintaining Good Vision
Hearing loss: due to melanocytes impairment in the inner ear.
Psychological disturbance: Stress, low self-esteem, and self-consciousness are common fallouts. In such conditions, you must consult a qualified psychologist and accept the situation by participating in support groups, talking to friends, family, and doctors.
Susceptible to autoimmune diseases: Vitiligo patients are susceptible to other autoimmune conditions such as Hashimoto’s disease, scleroderma, lupus, Addison’s disease, type-1 diabetes, pernicious anemia, etc.
Vitiligo is not a life-threatening condition, and though it can’t be cured, its progression can be controlled. However, it can considerably affect mental health. One must seek immediate medical advice when they notice discoloration on their bodies. People who face psychological distress need to seek help in order to help themselves accept the condition.
References
1. Vitiligo. NIH. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/vitiligo#tab-causes (accessed May 26, 2021).
2. Vitiligo: Overview. American Academy of Dermatology Association. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/vitiligo-overview (accessed May 26, 2021).
3. Vitiligo and Loss of Skin Color. WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/guide/vitiligo-common-cause-loss-skin-pigment (accessed May 26, 2021).
4. Vitiligo. MayoClinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/vitiligo/symptoms-causes/syc-20355912#:~:text=Vitiligo is a condition in,of skin color in patches (accessed May 26, 2021).
5. Brazier Y. Understanding the symptoms of vitiligo. Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/245081 (accessed May 26, 2021).
6. Scientists Implicate Gene in Vitiligo and Other Autoimmune Diseases. NIH. https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/scientists-implicate-gene-vitiligo-other-autoimmune-diseases (accessed May 26, 2021).
7. Roth E. What Is Vitiligo? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/skin-disorders/vitiligo-pictures (accessed May 26, 2021).
8. Vitiligo. NHS. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitiligo/ (accessed May 26, 2021).
9. Moghaddam AY, Sayyah M, Fini EA, et al. Investigation the Relationship between Skin Involvement Severity and Hearing Loss Severity in Vitiligo Patients. Mater Sociomed 2018; 30: 29–31.
10. Krüger C, Schallreuter KU. A review of the worldwide prevalence of vitiligo in children/adolescents and adults. Int J Dermatol 2012; 51: 1206–12.